Metal Additive Manufacturing: An Alternative to Traditional Methods?
- 77 Teknik

- Aug 18
- 4 min read

Shaping the Future of Metal Production
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, Metal Additive Manufacturing (Metal AM) has emerged as a truly disruptive technology, reshaping the way components are designed and produced. Unlike traditional methods such as machining, casting, and forging, where material is either removed or shaped from a solid block or molten metal, Metal AM creates parts layer by layer directly from metal powders, often using laser or electron beam energy to fuse the material. This approach enables the production of highly complex geometries that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve with conventional techniques.
Beyond design freedom, Metal AM offers significant material efficiency, drastically reducing waste by using only the metal required for the part itself. It also allows for lighter, yet stronger structures through optimized lattice designs, integrates multiple components into a single part to reduce assembly needs, and shortens lead times by eliminating the need for specialized tooling. These advantages make it an attractive option in industries such as aerospace, medical implants, automotive, and energy, where performance, customization, and efficiency are critical.
Furthermore, Metal AM supports rapid prototyping, enabling engineers to quickly test and refine designs, and facilitates on demand production, reducing inventory costs. As the technology matures, improvements in print speed, material diversity, and post processing techniques are steadily expanding its role from prototyping into full scale productio
At 77 Teknik, we see metal AM not as a complete replacement for traditional methods, but as a powerful complementary process for specific applications in aerospace, defense, automotive, and medical industries.
What Is Metal Additive Manufacturing?
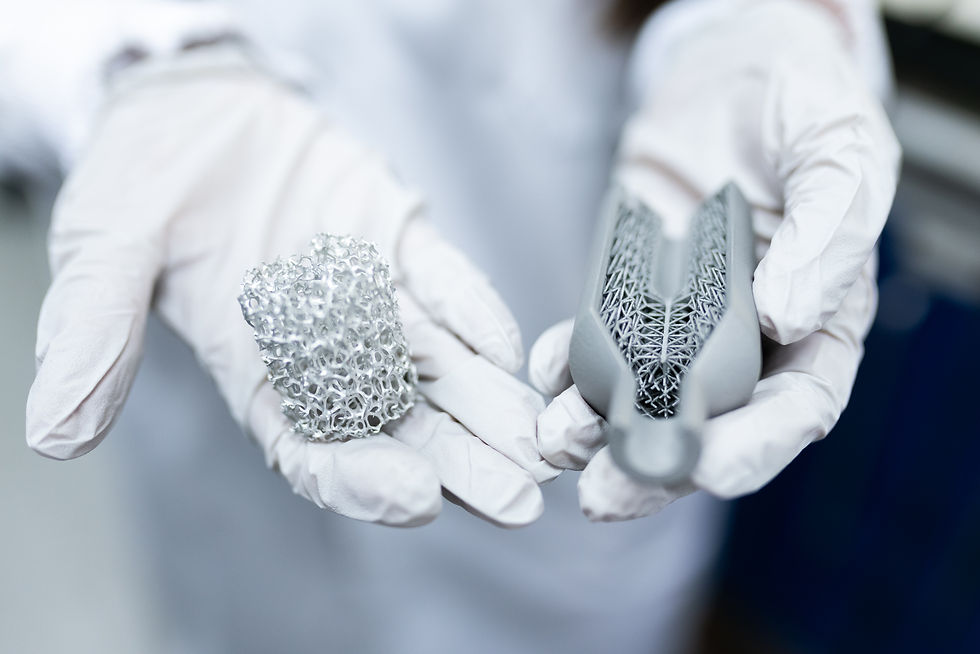
Metal additive manufacturing, often referred to as metal 3D printing, is a production method that fabricates solid metal components directly from a digital design. Instead of starting with a solid block and cutting away material, as in traditional subtractive manufacturing, this approach deposits material only where it is required. By building a part layer upon layer, it becomes possible to achieve intricate shapes and internal structures that would be extremely difficult, or even impossible, to create using conventional machining, casting, or forging.
How the Process Works
The workflow begins with a 3D model created in computer aided design (CAD) software. This model is digitally “sliced” into extremely thin cross sections by dedicated processing software. The additive manufacturing machine then interprets these slices as instructions for constructing the part layer by layer. The feedstock is typically a fine metal powder or, in some cases, a continuous metal wire.
Several core technologies are used in metal additive manufacturing, including:
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) – A thin layer of metal powder is spread over a build platform, and a focused energy source such as a laser or electron beam selectively melts the material according to the slice data. The platform then lowers, another layer of powder is applied, and the cycle repeats until the part is complete.
Binder Jetting – Instead of melting the powder directly, a liquid binder is deposited to bond the metal particles in the shape of each layer. Once printing is finished, the “green” part undergoes sintering in a furnace, which removes the binder and fuses the particles into a dense, solid structure.
Directed Energy Deposition (DED) – A nozzle feeds metal powder or wire directly into a melt pool created by a laser, electron beam, or plasma arc. This method is often used to build large components, repair worn areas, or add features to an existing part.
Key Advantages of Metal Additive Manufacturing
Greater Design Flexibility – Complex lattices, internal channels, and organic geometries can be produced without the limitations of traditional tooling.
Material Efficiency – Because material is only placed where it is needed, waste is minimal a major cost advantage when working with high value metals like titanium or Inconel.
Part Integration – Assemblies that would typically require multiple components can be printed as a single, consolidated part, reducing both weight and assembly time.
Accelerated Development – Prototypes and small batch production runs can be manufactured directly from a digital file, avoiding the delays and expense of tooling fabrication.
Customization Potential – Components can be tailored to specific performance requirements or user needs without incurring significant extra cost.
Advantages over traditional methods include:
Ability to produce complex, lightweight structures
Minimal material waste compared to subtractive manufacturing
Faster prototyping cycles
Potential for on demand production without extensive tooling
Metal AM vs Traditional Manufacturing
Criteria | Metal AM | Traditional Methods |
Design Freedom | High – intricate shapes possible | Limited by tooling and mold design |
Material Usage | Highly efficient – low waste | Often high waste in subtractive processes |
Lead Time | Short for small runs and prototypes | Longer due to tooling and setup |
Strength & Durability | Improving with material development | Proven track record with consistent quality |
Cost Efficiency | Better for low volume or complex parts | Better for high volume standardized parts |
77 Teknik’s Approach to Metal AM
We integrate metal AM into our manufacturing portfolio strategically:
Rapid Prototyping: Testing new designs in days instead of weeks.
Complex Component Production: Creating lightweight yet strong parts for aerospace and motorsport applications.
Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining metal AM with CNC machining for high precision finishing.
Repair & Refurbishment: Restoring high value components with targeted metal deposition.
Is Metal AM a Replacement?
While metal AM offers transformative advantages, it’s not always the most cost ffective or practical choice for high volume production. Traditional methods remain essential for mass manufacturing, but AM shines in low volume, complex, and high performance applications.
At 77 Teknik, we blend the best of both worlds, using each technology where it delivers the most value.
Let’s Discuss Your Next Project
Interested in exploring how metal additive manufacturing can enhance your product design and production efficiency?